May. 26, 2022
Pipe fittings are essential components that connect, extend, or change the direction of pipelines. By using different types of fittings, engineers can design safe and efficient piping systems for water, gas, oil, fire protection, HVAC and many other applications.
Each type of pipe fitting has a specific function: some change direction, some create branches, some reduce pipe size, and others stop the flow or allow easy disassembly. Choosing the right fitting type directly affects system safety, pressure performance, installation time and maintenance cost.
In this guide, we explain the main types of pipe fittings and their uses, and then focus on why galvanized malleable iron fittings are a reliable choice for plumbing and industrial pipelines. Galvanized pipe fittings are essential components in plumbing and industrial piping systems.
Compared with ordinary iron fittings, galvanized pipe fittings are more durable and reliable in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals. They are widely used in residential plumbing, construction projects, agriculture irrigation, oil and gas pipelines, and fire protection systems.
For international buyers, galvanized fittings are also compatible with other piping materials such as malleable iron, stainless steel, and brass, offering flexible solutions for different applications.
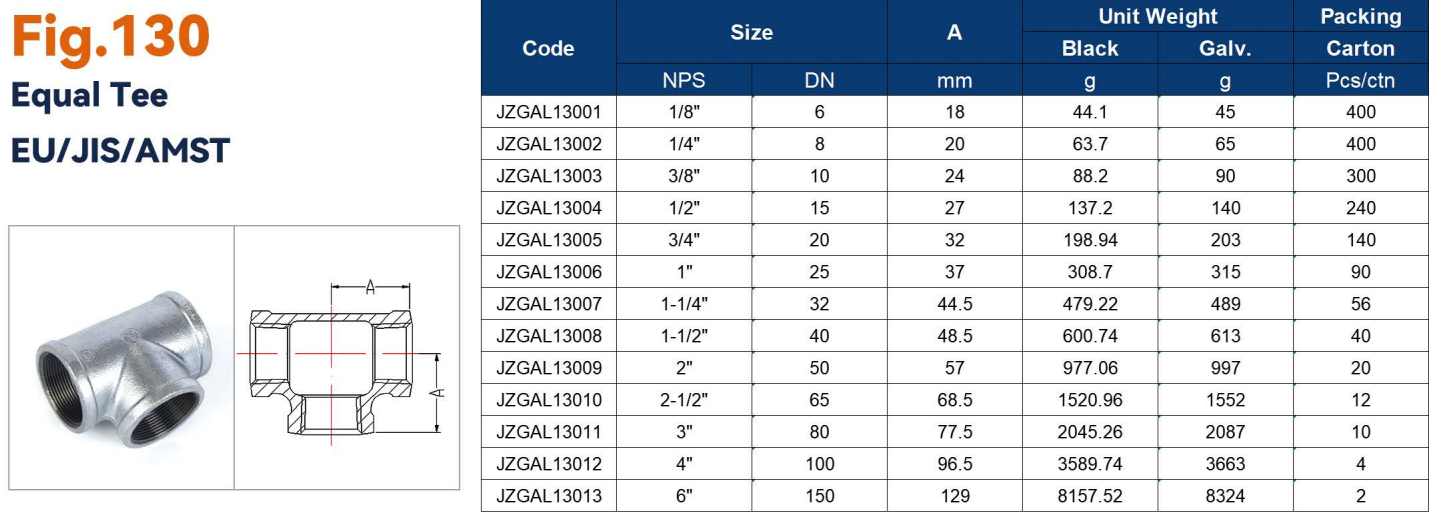
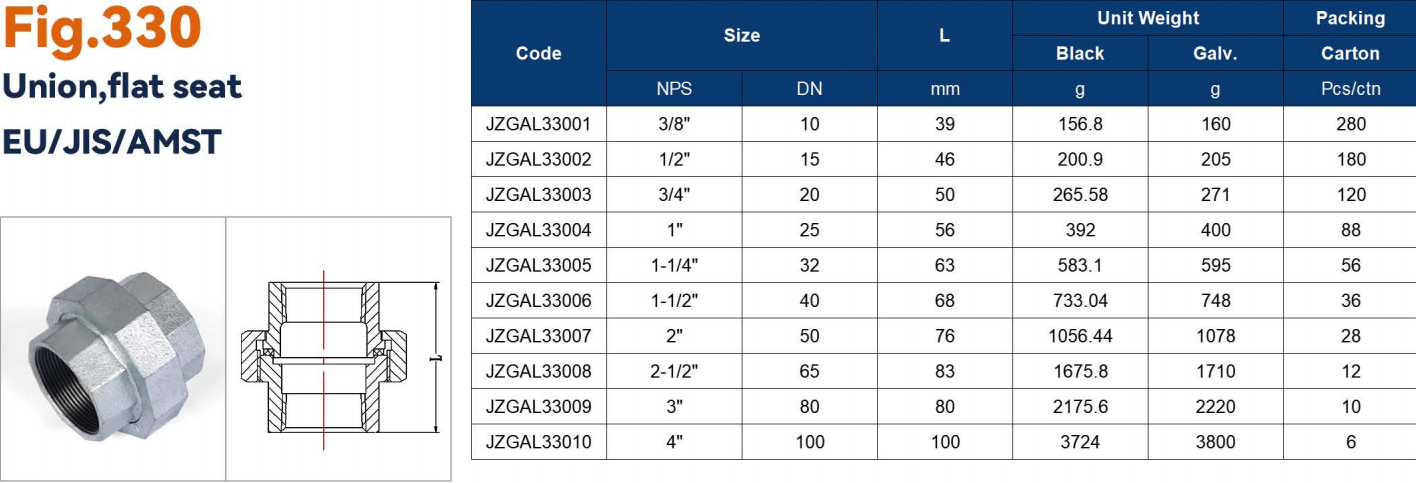
And in terms of the sizes and shapes of galvanized pipe fittings,there are including: bushings, elbows, couplings, caps, tees, unions, and hex plugs
Get the pipe fittings types data sheet
There are many ways to classify pipe fittings. The most practical way for buyers and engineers is to look at what each type does in the system:
● Fittings that change direction
● Fittings that change pipe size
● Fittings that connect or disconnect pipes
● Fittings that create branch lines
● Fittings that close or seal a line
● Special fittings for high-pressure or special equipment
Below is a quick overview of the most common types of fittings:
| Fitting Type | Main Function | Typical Connection | Common Materials | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elbow | Change flow direction | Threaded / welded / grooved | Galvanized malleable iron, carbon steel, stainless steel | Plumbing, gas supply, fire protection |
| Tee | Create branch connections | Threaded / grooved | Galvanized malleable iron, steel | Water distribution, sprinkler systems |
| Reducer | Connect different pipe sizes | Threaded / welded | Galvanized malleable iron, steel | Industrial pipelines, process lines |
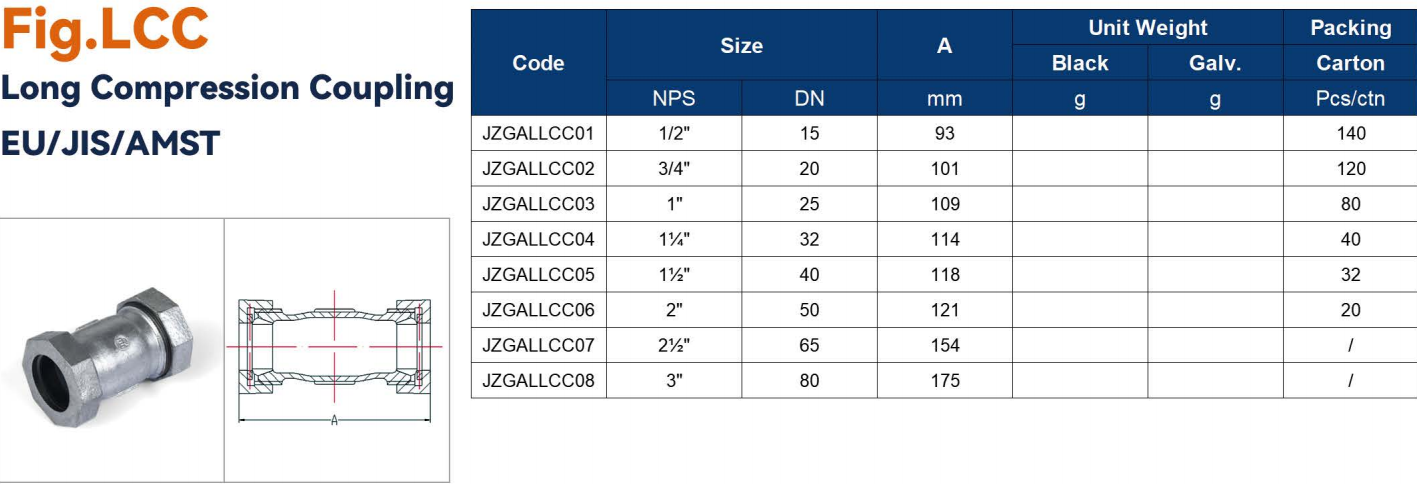
| Coupling | Connect two pipe ends | Threaded / grooved | Galvanized malleable iron, steel | Long pipelines, repairs |
| Union | Connect and easily disconnect pipes | Threaded | Galvanized malleable iron | Maintenance and frequent disassembly |
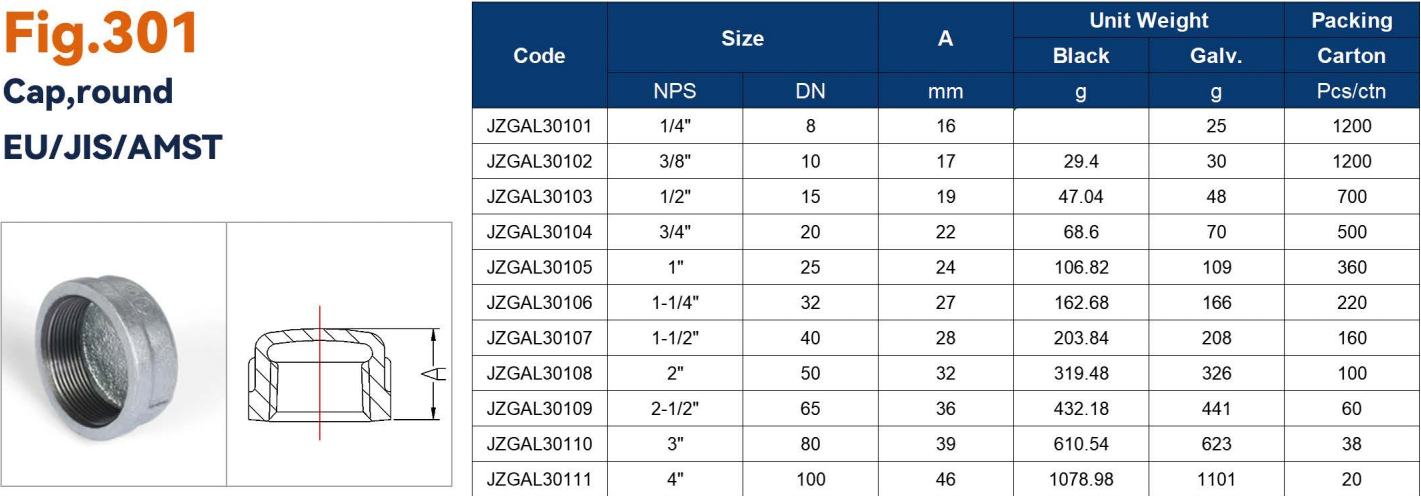
| Cap / Plug | Stop flow and close pipe end | Threaded | Galvanized malleable iron, steel | Temporary or permanent closure |
| Cross | Four-way branch | Threaded / grooved | Galvanized malleable iron | Fire protection networks |
| Nipple | Extend pipe or connect fittings | Threaded | Galvanized malleable iron, steel | Plumbing connections |
| Flange | High-pressure connection with bolts | Welded / flanged | Carbon steel, stainless steel | Oil & gas, chemical plants, power stations |
In the next sections, we look at each functional group of fittings types in more detail.
Galvanized malleable iron pipe fittings connect to piping for transporting fuel oil, water, gas, and other liquids for chemical, waste incineration, and semiconductor industry applications. These fittings are pipe with thick walls, impregnated with a protective zinc coating that protects against rust, corrosion, and mineral buildup and withstands wet conditions. The female threads are located on the inside of the fitting. The male threads are located on the outside of the fitting and screwed into the female threads. Threaded connections include NPT (American Standard Threads) or BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) and are sealed with PTFE tape retention. Threaded galvanized pipe fittings are available in a variety of sizes and shapes.
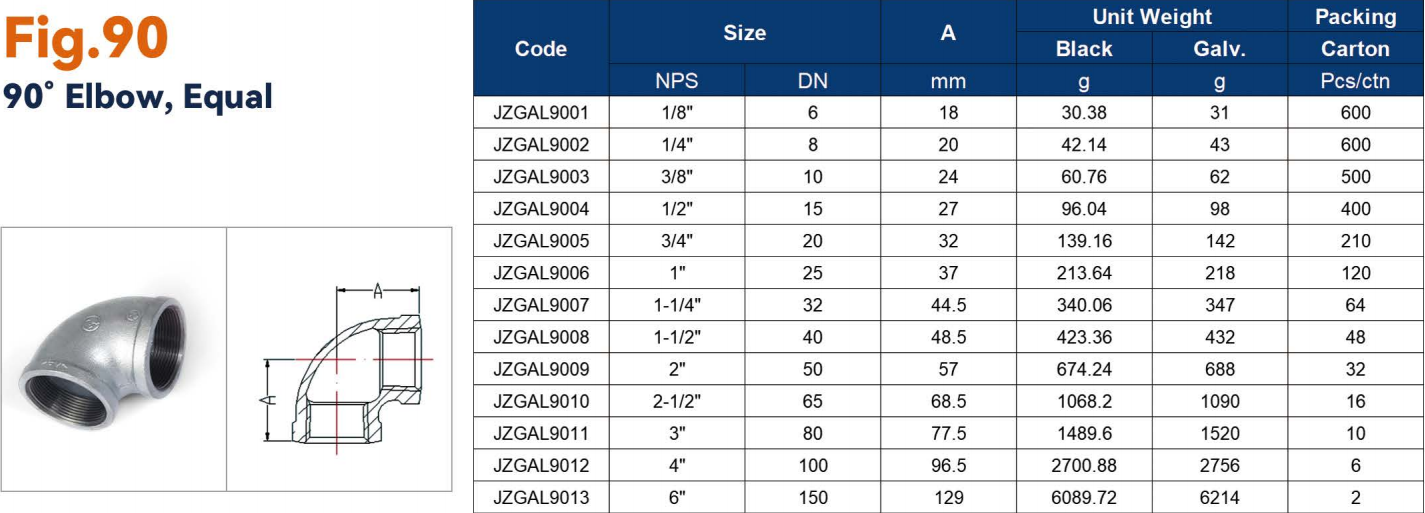
Galvanized elbows are available in two different sizes, 45 degrees and 90 degrees. This type of fitting is typically used for the water flow. The connection will be directly connected to the pipe. There are also 45-degree and 90-degree street elbows. Unlike regular elbows, street elbows are attached to galvanized fittings rather than the pipe itself and are also used to change the direction of the pipe.
Galvanized Couplings are typically used for join two tubes together. Couplings form a tight fit to prevent any leaks.This type of fitting is typically used for
Used to form airtight safety caps for the ends of galvanized pipes.
Used to combine or separate fluid flows, galvanized fittings are the perfect solution for adding to piping systems to connect pipes of different diameters or when pipes need to run in different directions.
Often confused with couplings, unions connect two pipes. The difference between the two is that unions provide a faster and easier way to disconnect a pipe in the event that maintenance is required.
Cross fittings connect four pipes at right angles, forming a “+” shape. They are commonly found in fire protection systems and water distribution networks.
Pipe nipples extend connections between fittings, while bushings reduce pipe size. They are practical in plumbing maintenance and small-scale pipeline adjustments.
Flanges are heavy-duty fittings used for high-pressure industrial applications. They allow secure connections between pipes, valves, or equipment, often in oil, gas, and chemical industries.
| Fitting Type | Function | Common Sizes | Pressure Rating | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elbow | Changes pipeline direction | 1/2" – 4" | Up to 150 PSI | Plumbing, gas systems, fire protection |
| Tee | Creates a branch connection | 1/2" – 6" | Up to 150 PSI | Water supply, agriculture, sprinkler systems |
| Union | Allows disassembly | 1/2" – 2" | Up to 150 PSI | Equipment connections, maintenance, repair |
| Coupling | Connects two pipes | 1/2" – 6" | Up to 150 PSI | Long pipelines, extensions |
| Reducer | Connects different diameters | 1/2" – 4" | Up to 150 PSI | Industrial piping, industrial piping, process lines |
| Cap/Plug | Seals pipe ends | 1/2" – 4" | Up to 150 PSI | Temporary or permanent closure |
| Cross | Four-way connection | 1/2" – 3" | Up to 150 PSI | Fire protection systems |
| Flange | High-pressure connection | 2" – 12" | 150–300 PSI | Oil, gas, industrial plants |
● Plumbing and Water Supply – Reliable connections for residential and commercial buildings.
● Gas and Oil Pipeline – Used in distribution networks due to durability.
● Fire Protection Systems – Cross and tee fittings ensure reliable water distribution.
● Agriculture Irrigation – Rust-resistant and suitable for outdoor installations.
● Construction & Infrastructure – Widely used in HVAC, drainage, and utility projects.
By choosing the correct types of fittings for each application, system designers can reduce maintenance, minimize leaks and extend the service life of the entire pipeline.
When selecting galvanized pipe fittings, buyers should consider:
☑ Material – Galvanized, malleable iron, brass, or stainless steel depending on environment.
☑ Connection Type – Threaded pipe fittings, compression fittings, grooved couplings, or welded connections.
☑ Project Requirements – Pressure rating, temperature resistance, and corrosion protection.
This ensures cost efficiency while meeting local industry standards.
Our galvanized malleable iron pipe fittings are produced and tested according to major international standards, including:
→ Standards: EN 10242, ANSI / ASME B16.3, DIN 2950, ISO 49, NBR 6943, IS 1879, BS EN 10242
→ Thread Standards: EN 10226, ASME B1.20.1, DIN 2999, ISO 7-1, ISO 228, IS 554
By following these standards, we ensure consistent quality, reliable working pressure and compatibility with global pipeline systems.
Hot-dip galvanizing is to make the molten metal react with the iron matrix to produce an alloy layer so that the matrix and the coating are combined. The hot-dip galvanizing step for pipe fittings is to first degrease the pipe fittings, and then pickling to remove iron oxide on the surface of the steel pipe. Then, the pipe fittings are immersed in a plating tank where zinc has been heated and melted in advance, and a zinc coating is formed on the surface of the pipe fittings, and finally, it can be lifted out.
Hot dip galvanizing is a chemical treatment. A complex chemical reaction occurs between the base of the pipe fitting and the molten zinc to form a zinc-iron alloy layer with corrosion resistance and a compact structure. The alloy layer is integrated with the pure zinc layer and the pipe fitting matrix. Therefore, Hot dip galvanized pipe fittings have strong corrosion resistance.
Hot-dip galvanized malleable iron pipe fittings
Cold galvanizing is also called electro-galvanizing. The amount of galvanizing is very small, only 10-50g/m2, and the zinc layer is independently layered from the base of the pipe fittings. Electrolytic galvanizing is to use electrolysis to make the zinc layer simply adhere to the base of the pipe fittings, and it is easy to fall off, so its corrosion resistance is poor.
The step of cold galvanizing for pipe fittings is to first degrease and pickle the pipe fittings, and then use electrolysis equipment to put them into a solution of zinc salt, and connect the negative electrode of the electrolysis equipment. A zinc plate is placed on the opposite side of the pipe and connected to the positive pole of the electrolysis device. When the power is turned on, the zinc ions move in the direction of the current from positive to negative, depositing on the pipe fittings. Cold galvanizing is a physical treatment, just brush a layer of zinc on the surface, so the zinc layer of pipe fittings is easy to fall off.
Although it is difficult to see the difference between the type of pipe fittings on the surface, in essence, they are very different.
Hot-dip galvanized pipe fittings have the advantages of uniform coating, strong adhesion, and long service life. In terms of zinc layer thickness, hot-dip galvanizing is dozens of times that of cold galvanizing, and the corrosion resistance is also dozens of times that of electro-galvanizing.
Electro-galvanized pipe fittings have a low cost, relatively cheap price, and a delicate and bright appearance.
Hebei Jianzhi Casting Group, following years of research and development, has made a significant breakthrough in electro-galvanizing, making the surface of electro-galvanizing almost the same as that of hot-dip galvanizing. This technology has been granted a Chinese design patent. The figure below illustrates a display of hot-dip galvanized pipe fittings and electro-galvanized pipe fittings produced by Hebei Jianzhi Casting Group.

Jianzhi galvanized pipe fittings
Hot-dip galvanizing is suitable for pipe fittings for outdoor work, such as outdoor sports facilities, power towers, bridges, and other large-sized fasteners that require long-term rust resistance. Electro-galvanizing is generally used for rust prevention of small-sized fasteners and pipes for indoor use.

galvanized malleable iron pipe fittings for Canton Tower

galvanized malleable iron pipe fittings for Beijing National Stadium
Founded in 1982, Jianzhi is a leading manufacturer and supplier of Galvanized Pipe Fittings. Till now, Jianzhi has about 4,500 employees and more than 350 technical engineers with distributors covering over 100 countries around the world. Jianzhi is committed to building a safer world by bringing premium Galvanized Pipe Fittings to every household and building .
Galvanized pipe fittings are essential for modern piping systems, offering durability, corrosion resistance, and a wide range of applications. Whether for plumbing, irrigation, fire protection, or industrial projects, choosing the right fittings ensures efficiency and long-term performance.
As a professional manufacturer of galvanized and malleable iron pipe fittings, we provide products that meet international standards and customer-specific requirements.
Standard: EN10242 /ANSI / ASME B16.3 / DIN2950 / ISO 49 / NBR6943 / IS1879 / BS EN10242
Threaded Standard: EN 10226 / ASME B.1.20.1 / DIN2999 / IS07-1 / IS0228 / IS554 / BS EN 10226
Galvanized fittings have average thickness of 86µm minimum or average coating weight of 610 g/m'
Q1: What are the main types of pipe fittings?
A: The main types of pipe fittings include elbows, tees, reducers, couplings, unions, crosses, caps, plugs, nipples, bushings, flanges, and valves. Each type of fitting has a specific function such as changing direction, branching, reducing pipe size, or stopping the flow.
Q2: Which types of fittings are best for outdoor or corrosive environments?
A: For outdoor pipelines and corrosive environments, galvanized malleable iron fittings are usually the best choice. Their thick zinc coating protects the steel from rust and extends the service life of elbows, tees, unions, and other fittings used in water, gas, and fire protection systems.
Q3: How do I select the right type of fitting for my pipeline?
A: Start from the function you need (direction change, branch, size reduction, closure), then consider pressure, temperature, medium, and environment. For most plumbing and industrial projects, threaded galvanized fittings are a safe and cost-effective option.
Q4: What is the lifespan of galvanized pipe fittings?
A: Typically 20–50 years depending on usage and environment.
Q5: Can galvanized pipe fittings be used with PVC or PEX?
A: Yes, with proper adapters, but galvanized fittings are most effective with metal pipes.
Q6: Are galvanized fittings suitable for high-pressure applications?
A: Standard galvanized fittings are for low to medium pressure. For high pressure, flanges or welded fittings are recommended.
Q7: What is the MOQ and lead time?
A: Minimum order quantity and delivery time can be customized based on buyer requirements.
Q8: Do you provide OEM/ODM services?
A: Yes, customized production and branding are available for international clients.
Looking for the best-galvanized pipe fittings online?
You have come to the right place. JIANZHI leading factory of malleable cast iron pipe fittings and galvanized pipe fittings, we can offer you high-quality products at competitive prices. We supply quality galvanized pipe fittings to North America, Europe, the Middle East, pipe fittings types include elbows, nipples, tees, nipples, nuts, caps, crosses, elbows, flanges and nipples. we also cover your sizes, details can be found by clicking on our specific products or contacting.
SAFER
PRODUCT INFO
ABOUT JIANZHI
TECH DATA
Contact Us
E-mail: sales1@jianzhi-fitting.com
Tel: +86 15822792427
Office In Tianjin:
Heping District, Tianjin, China.
Production Base 1:
Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, China.
Production Base 2:
Tangshan City, Hebei Province, China.
Production Base 3:
Schelei Street,Baicoi City,Prahova County,Romania