Dec. 25, 2025
This article provides a comprehensive technical analysis of black malleable iron pipe fittings, focusing on the industry-leading manufacturing standards of Hebei Jianzhi Casting Group Co., Ltd. Since 1982, Jianzhi has evolved into a global powerhouse, employing over 4,000 professionals across 400,000 square meters. We explore the mechanical properties, threading precision (BSPT/NPT), and the specific performance metrics that define high-quality black pipe fittings. By integrating engineering formulas with practical application data, this guide serves as a definitive resource for procurement officers and mechanical engineers.

● Material Integrity: Black pipe fittings are preferred for gas and oil lines due to their high tensile strength and impact resistance.
● Precision Threading: Proper seal integrity depends on the mathematical accuracy of taper threads (1:16 ratio).
● Cost-Efficiency: Jianzhi fittings utilize advanced annealing processes to ensure zero-defect installation, reducing long-term labor costs.
● Global Compliance: Adherence to ISO 7-1 (BSPT) and ASME B1.20.1 (NPT) ensures cross-border compatibility.
1. Executive Summary
2. Introduction: The Role of Black Malleable Iron in Modern Piping
3. Technical Fundamentals: Material Composition and Geometry
4. Performance Analysis: Pressure Ratings and Calculation Models
5. Measuring and Standardizing: BSPT vs. NPT Threading Systems
6. The Jianzhi Advantage: Manufacturing Excellence Since 1982
7. Advanced Comparisons: Malleable Iron vs. Other Casting Materials
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
9. Final Reflection: The Craftsmanship of Casting
10. References
In the modern industrial landscape, the reliability of fluid and gas conveyance systems depends heavily on the quality of connections. Hebei Jianzhi Casting Group, a titan of the industry since 1982, specializes in the production of high-grade black pipe fitting components. Our facility, one of the largest in China, employs 4,000+ professionals dedicated to the "Heavy Type" design philosophy—where wall thickness and material density are prioritized over cost-cutting.
This guide explains why malleable iron pipe fitting products remain the preferred choice for engineers in high-vibration and high-pressure environments. We breakdown the metallurgy of the annealing process, the geometry of our various product types (elbows, tees, unions), and provide the mathematical proof of their durability.
In the complex architectural and industrial anatomy of the 21st century, piping systems serve as the critical circulatory network of our civilization. Whether transporting volatile natural gas to urban centers, circulating high-pressure steam in manufacturing plants, or providing the backbone for fire suppression in high-rise skyscrapers, the integrity of these systems is paramount. At the heart of these networks lies the black pipe fitting—a component that, while often hidden from public view, represents centuries of metallurgical evolution and engineering refinement. To understand the significance of Hebei Jianzhi Casting Group’s role in this industry, one must first understand the unique functional and structural role that black malleable iron plays in the modern world.
The term "black pipe fitting" is frequently used in the trade, yet its technical origin is often misunderstood by those outside the engineering community. The "black" designation does not merely refer to an aesthetic choice; it refers to the dark iron-oxide scale that naturally forms on the surface of the malleable iron during the intense heat of the casting and annealing processes.
Unlike galvanized fittings, which are coated with a layer of zinc to prevent oxidation, black fittings are typically finished with a light coating of protective oil or a thin lacquer. This specific finish is a strategic engineering requirement. In many applications—particularly those involving the transport of natural gas—the presence of zinc can be detrimental. Over time, gas can react with a galvanized coating, causing the zinc to flake off and enter the gas stream, where it can clog sensitive burners, valves, and pilot lights. Thus, the black pipe fitting is not an "uncoated" version of a galvanized fitting, but a specialized component designed for chemical compatibility with the fluids it carries.
To appreciate the malleable iron pipe fitting, we must contrast it with the standard cast iron pipe fitting of the early industrial era. Traditional grey cast iron is characterized by its high carbon content and the presence of graphite in flake form. While excellent for compression-heavy applications like engine blocks or manhole covers, grey iron is notoriously brittle. Under the stress of thermal expansion, sudden mechanical impact, or high-pressure surges, grey iron can shatter without warning.
The introduction of "malleability" changed the trajectory of piping history. Through a sophisticated metallurgical process of controlled heating and cooling (annealing), the carbon flakes in the iron are transformed into spherical nodules. This microscopic shift has macro-level consequences: it allows the metal to absorb energy and deform plastically before failure. In modern piping, where buildings "breathe" and industrial machinery vibrates, a black pipe fitting acts as a resilient joint rather than a brittle point of failure. This toughness is the "Jianzhi Standard"—a commitment to a material that can withstand the unpredictable stresses of a dynamic environment.
Why, in an age of advanced polymers and composite plastics, do we continue to rely on malleable iron pipe fitting products? The answer lies in the unique demands of modern infrastructure:
In the event of a structural fire, a building’s survival often depends on its sprinkler system. Plastic pipes and fittings, while inexpensive and easy to install, have low melting points and can emit toxic fumes when burned. A cast iron pipe fitting, specifically one made of black malleable iron, can withstand extreme temperatures for prolonged periods, ensuring that water continues to flow through the fire suppression system even as the building’s environment reaches critical heat levels. Jianzhi’s UL and FM-certified black fittings are specifically engineered for this life-saving reliability.
As global energy grids shift toward natural gas and hydrogen blends, the containment of these gases requires materials with zero porosity. The high-pressure Disamatic molding used by Jianzhi ensures that every black pipe fitting has a dense, uniform molecular structure. This prevents the "seepage" common in lower-quality sand-cast fittings. In the gas industry, the word "malleable" is synonymous with "security."
Modern industrial facilities are filled with reciprocating pumps, massive compressors, and high-velocity fluid flows. These create constant micro-vibrations that can cause steel pipes to suffer from fatigue. Because of the "temper carbon" nodules within a malleable iron pipe fitting, the material possesses a natural damping capacity. It absorbs the energy of these vibrations, protecting the threaded joints from loosening or cracking over decades of service.
When procurement officers evaluate black pipe fitting options, there is often a temptation to choose the lowest-priced "Light Type" fitting. However, the introduction of Jianzhi’s "Heavy Type" philosophy into the market has shifted the conversation from "initial cost" to "lifecycle value."
A low-quality, thin-walled cast iron pipe fitting is prone to "wrench-cracking" during installation—a failure that can stall a multi-million dollar construction project for days. Furthermore, the long-term cost of a leak—measured in property damage, environmental fines, and system downtime—far outweighs the marginal savings of a cheaper fitting. Jianzhi’s manufacturing excellence ensures that the "Total Cost of Ownership" (TCO) is minimized through durability and a 0% leakage rate.
The role of black malleable iron in modern piping is also defined by its ability to cross borders. In the 19th century, every foundry had its own threading patterns, making repairs nearly impossible. Today, the global economy relies on the standardization that Jianzhi has mastered. By providing both BSPT (British Standard) and NPT (American Standard) threading, we ensure that a black pipe fitting manufactured in our Hebei facility can seamlessly integrate into a refinery in Singapore, a school in London, or a high-rise in Chicago. This interoperability is the silent engine of global trade.
As we move into 2025 and beyond, the role of materials in the circular economy has become a primary concern for engineers. Unlike plastic (PEX or PVC) fittings, which are petroleum-based and difficult to recycle, malleable iron pipe fitting products are 100% recyclable. Most of the raw material used in a Jianzhi black pipe fitting comes from recycled scrap steel and iron, which is then refined and cast into a new, long-lasting component. When a building is eventually decommissioned, the iron fittings can be melted down and repurposed indefinitely, making them a cornerstone of sustainable construction.
In the world of mechanical engineering, a catalog is more than a list of parts—it is a map of solutions. For Hebei Jianzhi Casting Group, our catalog represents over 40 years of iterative design, encompassing more than 2,000 individual SKUs. Each malleable iron pipe fitting is engineered to balance three critical factors: fluid dynamic efficiency, structural thickness, and threading precision.
While many manufacturers prioritize the reduction of raw material to lower costs, Jianzhi adheres to the "Heavy Type" philosophy. This ensures that every fitting exceeds the minimum weight and wall thickness requirements of international standards like EN 10242 and ASME B16.3. Below is an exhaustive technical breakdown of our product categories and their specific geometric advantages.
Directional fittings, primarily elbows and bends, are the most frequently used components in any piping network. Their primary role is to redirect flow while maintaining pressure integrity.
The geometry of a Jianzhi black pipe fitting elbow is defined by its "Sweep." A sharp internal corner creates turbulence, which leads to pressure drops and localized erosion. Jianzhi elbows feature a precision-cast internal radius that promotes laminar flow.
● The 90° Elbow: Used for right-angle turns. Our "Banded" design provides extra material at the female thread entry to prevent "splitting" when high torque is applied during installation.
● The 45° Elbow: Essential for navigating complex architectural bypasses. The 45° angle reduces the hydraulic shock (Water Hammer) compared to a 90° turn.
The "Street Elbow" is a masterpiece of space-saving geometry. By featuring one male thread and one female thread, it eliminates the need for a separate pipe nipple, allowing for a direct connection to a pump or valve. Jianzhi ensures the concentricity of the male and female axes is perfect; if the axes are even 1° off, the entire pipe run will be crooked.
Branching fittings like Tees and Crosses are the most stressed components in a system because they must manage fluid forces coming from multiple directions simultaneously.
A Tee allows a 90° branch from the main line. At Jianzhi, our malleable iron pipe fitting tees are famous for their "Reinforced Crotch." The area where the branch meets the main run is the most common point of failure in low-quality cast iron pipe fitting products.
Reducing Tees: These allow the branch line to be a different diameter than the run. Casting a reducing tee is significantly more difficult than a standard tee because the varying wall thicknesses cool at different rates in the mold. Jianzhi’s 96-hour annealing process ensures that the internal stresses caused by this uneven cooling are completely neutralized.
Used primarily in fire sprinkler headers and complex industrial manifolds, the Cross is a four-way junction. Because it has four openings, the structural rigidity of the center "hub" is critical. Jianzhi Crosses are cast with a "Heavy Wall" specification to ensure they do not deform under the cumulative weight of long pipe runs.
These fittings are the "glue" that holds the linear sections of a system together.
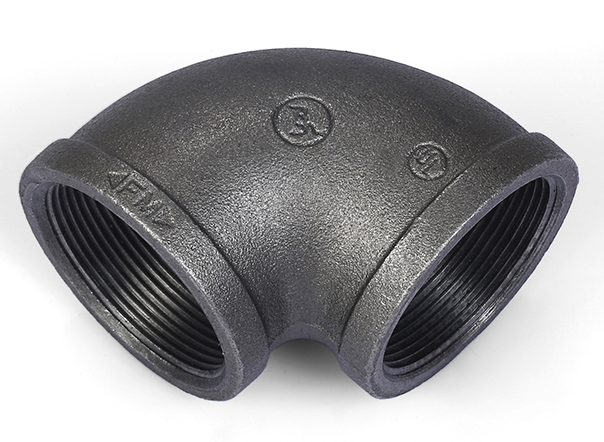

The coupling is a simple sleeve with internal threads. However, Jianzhi’s coupling geometry includes a "Tapered Lead-In." This subtle geometric feature allows the pipe to be started easily by hand, reducing the risk of cross-threading—a major cause of labor loss on construction sites.
When a pipe size must change, Bushings and Reducers are employed.
Hex Bushings: These feature a hexagonal head for easy wrenching. The geometry must be perfectly balanced; if the wall between the internal and external thread is too thin, it will crack. Jianzhi’s "Heavy Type" bushings provide 15-20% more metal in this critical "Bridge" area.
Reducing Sockets: These provide a more gradual transition between pipe diameters, which is hydraulically superior for high-velocity liquid lines.
A piping system must be maintainable. Without the proper termination and maintenance fittings, a simple pump failure could require the destruction of the entire pipe run.
The Union is the most complex black pipe fitting in the catalog. It consists of three separate pieces: the thread end, the bottom end, and the nut.Conical vs. Flat Seat: Jianzhi specializes in the "Conical Seat" (Iron-to-Iron) union. The geometry of the cone-to-socket fit must be machined to a tolerance of ± 0.01mm. When the nut is tightened, the two surfaces are "crushed" together to create a metal-to-metal seal that requires no gasket. This is the ultimate connection for high-pressure steam and gas.
Termination fittings like caps (female) and plugs (male) are used to seal the end of a line. While they seem simple, they must withstand the full "Dead-End" pressure of the system. Jianzhi plugs feature a "Square Head" or "Hex Head" designed to withstand high-torque removal even after years of corrosion.
One of the most significant specifications in our catalog isn't a part, but a geometric property: Squareness. In many low-end cast iron pipe fitting products, the threads are not perfectly aligned with the body of the fitting.
The Impact of Misalignment: If an elbow is 91° instead of 90°, over a 10-meter pipe run, the end of the pipe will be off-center by nearly 20 centimeters.
The Jianzhi Solution: Our automated CNC threading centers utilize laser-alignment sensors to ensure that every thread is cut at a perfect 90° or 45° angle to the fitting's axis. This "Squareness" ensures that installers don't have to "force" pipes into place, which introduces mechanical stress into the system.
To understand why Jianzhi is the preferred brand for foreign trade, we must look at the physical specifications. The following table illustrates the "Heavy Type" advantage for a standard 1-inch (DN25) black pipe fitting elbow.
Metric | Industry Standard (Light Type) | Jianzhi Heavy-Duty Spec | Engineering Benefit |
Wall Thickness ($t$) | 2.2 mm | 3.0 mm | Higher burst pressure; longer rust-through life. |
Weight (Approx.) | 260g | 315g | More material to absorb mechanical vibration. |
Thread Depth | 12 mm | 15 mm | More "Leads" for a secure, leak-proof seal. |
Tensile Strength | 300 MPa | 350 MPa | Ability to deform without cracking. |
Elongation Rate | 5% - 6% | 10% - 12% | Superior performance in seismic/vibration zones. |
In 2025, geometry isn't just physical; it’s digital. Jianzhi provides full 3D CAD and BIM (Building Information Modeling) files for our entire catalog. This allows engineers to simulate the flow dynamics and spatial requirements of our malleable iron pipe fitting products before the first stone is laid on a job site. Our digital specifications include:
● Center-to-End Dimensions: Critical for precise pipe cutting.
● Weight Data: Necessary for calculating the load on pipe hangers and supports.
● Hydraulic Resistance Coefficients ($K$ factors): Used for precise pump sizing and pressure-drop calculations.
A fitting’s geometry must be protected from the factory to the job site. Our specifications for foreign trade include:
● Anti-Rust Oil Coating: A proprietary black oil that maintains the "Black" finish while preventing oxidation during maritime transit.
● Double-Wall Corrugated Boxes: Designed to withstand the weight of high-density iron without collapsing.
● Thread Protectors: For large-diameter fittings, we use plastic inserts to ensure the BSPT or NPT threads aren't dinged during handling.
In the hierarchy of ferrous metals, the malleable iron pipe fitting occupies a unique and vital position. While standard cast iron pipe fitting products (grey iron) are often used for gravity-fed drainage or low-stress applications, the demands of high-pressure gas, steam, and hydraulic systems require a material that combines the castability of iron with the toughness of steel. This material is malleable iron.
At Hebei Jianzhi Casting Group, our reputation is built on an uncompromising understanding of metallurgy. We do not simply "melt and pour"; we engineer a material that undergoes a profound molecular metamorphosis before it ever reaches the threading line.
The performance of any iron-based black pipe fitting is determined primarily by the form and distribution of carbon within the iron matrix.
In traditional grey cast iron, carbon precipitates during cooling in the form of sharp, elongated flakes. These flakes act as internal "stress risers" or microscopic cracks. When the metal is subjected to tension or sudden impact, the stress concentrates at the tips of these flakes, causing the material to fracture. This brittleness makes grey iron unsuitable for pressurized gas or high-vibration environments.
Malleable iron solves this problem through a two-stage process. First, the iron is cast as "White Iron," where all carbon is chemically locked in the form of iron carbide ($Fe_3C$). This material is incredibly hard but lacks any ductility. Through Jianzhi’s proprietary heat treatment, this iron carbide is dissociated, and the carbon precipitates as "temper carbon" nodules—irregularly shaped clusters that do not interrupt the continuity of the iron matrix as flakes do. This allows the metal to deform slightly under stress rather than shattering, providing the "malleability" that the industry depends on.
The path to a high-quality malleable iron pipe fitting begins in our electric induction furnaces. Unlike smaller foundries that use traditional cupola furnaces with fluctuating temperatures, our electric melting process allows for the precise control of five critical elements.
Element | Specification | Technical Function in the Pipe Fitting |
Carbon (C) | 2.4% – 2.9% | Balances fluidity in the mold with post-annealing strength. |
Silicon (Si) | 1.4% – 1.6% | Acts as the primary graphitizing agent during heat treatment. |
Manganese (Mn) | 0.4% – 0.6% | Neutralizes sulfur and increases the toughness of the ferrite matrix. |
Sulfur (S) | < 0.12% | Kept strictly low to prevent "hot shortness" and brittle failure. |
Phosphorus (P) | < 0.15% | Controlled to ensure the metal remains ductile at sub-zero temperatures. |
We utilize the Carbon Equivalent (CE) formula to monitor the balance of our melt:
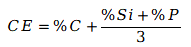
By maintaining a stable CE, Jianzhi ensures that every black pipe fitting has a consistent density, which is critical for preventing the "micro-porosity" that can lead to gas leaks.
When the molten iron is poured into our Disamatic high-pressure molds, it cools rapidly to form White Cast Iron. In this state, the microstructure is composed of pearlite and ledeburite.
● Mechanical State: Brittle and extremely hard (approx. 350-450 HB).
● Engineering Challenge: If you were to thread a white iron fitting, the tool would shatter, and the fitting would crack.
The white iron phase is a necessary "blank slate." It ensures that all carbon is evenly distributed in a combined state ($Fe_3C$) before we begin the long-cycle graphitization process.
Annealing is the soul of malleable iron pipe fitting production. While many "light-type" manufacturers attempt to shorten this cycle to 48 or 60 hours to reduce energy consumption, Jianzhi maintains a 72-to-96-hour cycle in our state-of-the-art tunnel kilns. This commitment to time is what separates a "commodity" fitting from an "engineered" fitting.
During the first stage, the fittings are heated slowly to approximately 950°C. At this temperature, the iron carbide begins to dissociate:
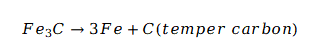
The primary cementite breaks down, and the carbon begins to aggregate into those vital temper carbon nodules. Shortening this phase leads to "incomplete graphitization," leaving brittle spots inside the fitting wall.
The cooling process from 760°C to 700°C is the most critical phase. We cool the fittings at a rate of only 3°C to 5°C per hour. This allows the remaining carbon to migrate out of the pearlite, leaving a matrix of pure, soft ferrite.
This slow cooling ensures that the black pipe fitting achieves a high elongation rate. While the standard requirement is often only 5%, Jianzhi’s metallurgy consistently achieves 10% to 12% elongation, providing an enormous safety margin for installers.
The result of this metallurgical rigor is a material that performs more like steel than iron. Our laboratory tests every batch of cast iron pipe fitting for the following metrics:
Tensile strength () measures the maximum stress the material can handle before breaking.
Jianzhi Standard: 330–350 MPa.Yield strength (σy) measures the point at which the material begins to deform permanently.
Jianzhi Standard: 200–230 MPa.This high yield strength ensures that when a plumber applies high torque with a pipe wrench, the malleable iron pipe fitting will hold its shape and maintain a tight seal without the threads stripping or the body cracking.
The Brinell Hardness of a Jianzhi fitting is kept below 150 HB. This is specifically optimized for high-speed CNC threading. A "soft" ferrite matrix allows the threading dies to cut clean, sharp, and consistent BSPT or NPT profiles. This reduces "chatter" during machining, resulting in a thread surface that is as smooth as glass, requiring less sealant to achieve a gas-tight joint.
It is a common question in foreign trade: Why not use ductile iron? While ductile iron is also tough, it achieves its properties "as-cast" by adding magnesium. This results in larger, perfectly spherical nodules. However, for small-diameter pipe fitting products (1/8" to 6"), malleable iron is superior because:
● Section Sensitivity: Malleable iron is less sensitive to varying wall thicknesses.
● Surface Finish: The annealing process results in a smoother surface finish, which is critical for the "Black" oil-coated aesthetic.
● Threading: Malleable iron’s microstructure is more consistent for the precision tapping required in tapered pipe threads.
Finally, Jianzhi’s metallurgy is supported by our "Heavy Type" design. By utilizing high-pressure Disamatic molding, we produce a casting that is significantly denser than traditional sand-cast fittings.
● Zero Porosity: In gas systems, "pinhole leaks" are the primary danger. A denser molecular structure means the black pipe fitting is naturally gas-tight even before any surface treatment is applied.
● Corrosion Resistance: The higher density and precise silicon content create a natural oxide layer that resists atmospheric corrosion better than low-grade "light" fittings.
Manufacturing excellence is the bridge between theoretical metallurgy and the high-performance reality of a black pipe fitting. At Jianzhi, our manufacturing philosophy is built on vertical integration and automated precision. By controlling every variable from the initial melt to the final thread coating, we eliminate the inconsistencies inherent in outsourced production. Our facility—the largest of its kind in China—serves as a global benchmark for how a cast iron pipe fitting should be produced.
The journey of a Jianzhi fitting begins not with metal, but with sand. We utilize the Disamatic (Denmark) vertical high-pressure molding system, which is the gold standard in automated foundry technology.
Unlike traditional manual sand casting, which relies on the skill of individual workers and is prone to human error, the Disamatic system uses high-pressure hydraulics to compress sand into ultra-dense molds.
● Dimensional Accuracy: The high-pressure mold ensures that the external geometry of the malleable iron pipe fitting is consistent within fractions of a millimeter.
● Core Stability: The "core" (the part that creates the hollow interior of the fitting) is locked into place with mechanical precision. This prevents "core shift," ensuring that the wall thickness of the elbow or tee is perfectly uniform. A uniform wall is critical for the safety of a black pipe fitting, as any thin spot becomes a point of potential rupture under pressure.
While the molds are being prepared, our melting department prepares the "White Iron" melt. Jianzhi has transitioned entirely away from traditional cupola furnaces to Electric Induction Furnaces.
Temperature Precision: We maintain the molten iron at a precise 1,500°C. Electric induction allows for instant temperature adjustments, ensuring the metal is fluid enough to fill the intricate details of a small-diameter pipe fitting mold without cooling prematurely (a defect known as "cold shut").
Automated Pouring: To ensure consistency, we use automated pouring ladles. By controlling the pour rate and volume, we minimize turbulence in the mold, which prevents air bubbles (gas porosity) from forming inside the casting.
Once the castings have cooled and the sand is "shaken out," they are technically white iron—brittle and unworkable. The most critical step in creating a malleable iron pipe fitting is the heat treatment.
Jianzhi utilizes massive, automated tunnel kilns that operate 24/7. As discussed in the metallurgy section, we adhere to a 96-hour cycle.
● Uniform Heating: The tunnel kiln design ensures that every fitting, whether at the top or bottom of the charging basket, experiences the exact same thermal curve.
● Atmosphere Control: We control the oxygen levels inside the kiln to prevent excessive "decarburization" or surface scaling, which preserves the clean finish of the black pipe fitting.
After annealing, the fittings are tough and ductile, but their surface is covered in heat-treatment scale. We use high-velocity shot blasting machines to pelt the fittings with tiny steel beads.
● Objective: This removes all oxides and creates a slightly textured surface that is ideal for the adherence of the protective black oil.
● Visual Inspection: This stage is the first of many human interventions. Our trained inspectors check for "mis-runs" or surface cracks that may have been hidden by sand.
The thread is the most important functional element of a malleable iron pipe fitting. If the thread is off-center, too shallow, or has the wrong taper, the joint will leak.
Jianzhi utilizes Automated Multi-Spindle CNC Threading Machines.
● Alignment: The fitting is clamped in a high-precision jig that aligns the axis of the fitting with the axis of the cutting tool. This ensures the "Squareness" of the joint.
● Tool Monitoring: Our CNC systems monitor the wear on the cutting dies. When a tool begins to dull—before it can produce a sub-standard thread—the system alerts the operator to change the die.
Standards Mastery: We can switch between BSPT (ISO 7-1) and NPT (ASME B1.20.1) configurations with the press of a button, ensuring that our black pipe fitting products meet the exact requirements of the destination country.
This is the "Jianzhi Guarantee." While many factories use statistical sampling (testing 1 in 100), Jianzhi tests 100% of its production.
● The Process: Each fitting is sealed at both ends, pressurized with 0.6 MPa of compressed air, and submerged in a water tank.
● The Standard: A single bubble escaping from the metal body or the thread area results in an immediate rejection. This rigorous testing is why Jianzhi has a reputation for "Zero Leaks" in the international natural gas industry.
The final stage is the application of the "Black" finish.
● The Coating: We use a proprietary, environmentally friendly rust-preventative oil. This oil penetrates the pores of the iron and the valleys of the threads, providing a barrier against moisture during ocean transit.
● Automated Packaging: Fittings are counted and bagged by weight-sensing machines to ensure accuracy in quantity. They are then packed into reinforced, double-walled corrugated boxes, designed to withstand the rigors of global shipping.
What makes the Jianzhi manufacturing process truly "excellent" is our scale. With 400,000 square meters of space and 4,000 employees, we are not just a factory; we are an industrial ecosystem.
● In-House Tooling: We design and manufacture our own molds and jigs in our dedicated machine shop.
● Raw Material Control: We source and test our own scrap and pig iron to ensure the chemical purity of the melt.
By maintaining this level of vertical integration, Jianzhi ensures that a malleable iron pipe fitting purchased in 2025 has the same metallurgical and dimensional perfection as one purchased in 1982. This consistency is the foundation of the "Jianzhi Advantage" in the global cast iron pipe fitting market.
In the field of fluid mechanics, a piping system is only as strong as its weakest connection. For engineers and system designers, selecting a black pipe fitting is not merely a matter of matching diameters; it is a rigorous exercise in calculating stress thresholds and safety margins. At Hebei Jianzhi Casting Group, our "Heavy Type" design philosophy is rooted in the mathematical certainty that extra material thickness translates directly into higher safety factors and longer operational lifespans.
In the international trade of malleable iron pipe fitting products, pressure is categorized into "Classes" defined by organizations like ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) and ISO.

Despite the "150" designation, these fittings are rated for significantly higher pressures at ambient temperatures. According to ASME B16.3, a Class 150 black pipe fitting is typically rated for:
300 PSI (2.0 MPa) for water, oil, or gas at temperatures between -20 ℉ and 150 ℉.
150 PSI (1.0 MPa) for saturated steam.
For high-pressure steam lines or deep-well oil applications, Jianzhi produces Class 300 fittings. These feature significantly thicker walls and reinforced bands, allowing for working pressures up to 1,000 PSI at ambient temperatures.
To determine the Maximum Allowable Working Pressure (MAWP) of a cast iron pipe fitting, Jianzhi engineers employ an adaptation of Barlow’s Formula. This formula relates the internal pressure of a cylinder to its physical dimensions and the strength of the material.
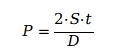
Where:
● P: Internal Pressure (PSI).
● S: Allowable Stress of the material (PSI). For Jianzhi malleable iron, we use a conservative allowable stress that accounts for the 4:1 safety factor.
● t: Minimum Wall Thickness (inches).
● D: Outside Diameter (inches).
By increasing the wall thickness (t) by just 10%–15% compared to "light-type" competitors, Jianzhi effectively increases the burst pressure threshold by a much larger margin, ensuring the fitting can handle unexpected "spike" pressures without catastrophic failure.
When a black pipe fitting is pressurized, the stress is not distributed evenly. Through Finite Element Analysis (FEA), Jianzhi technicians have identified the high-stress zones within common fitting geometries.
In a Tee fitting, the area where the branch meets the main run (the "crotch") experiences the highest concentration of stress. This is due to the interruption of the cylindrical geometry. Jianzhi "Heavy Type" Tees feature a reinforced radius at this junction, effectively redistributing the stress across a larger volume of metal and preventing the formation of fatigue cracks over time.
Most Jianzhi malleable iron pipe fitting products feature a "band" at the female thread entry. This is not purely aesthetic. When a male pipe is threaded into the fitting, it exerts a massive "wedging" force. The band acts as a structural hoop, resisting this expansion force and preventing the fitting from splitting during high-torque installations.
Static pressure is only half of the story. In real-world applications, such as fire protection or industrial cooling, valves open and close rapidly. This creates a shockwave known as Water Hammer.
● Impact Resistance: Unlike brittle grey cast iron pipe fitting products, malleable iron possesses the ductility to absorb the kinetic energy of a pressure surge. The material "gives" slightly under the shockwave, whereas a brittle material would shatter.
● Safety Factor: Jianzhi products are tested to a burst pressure of at least 4 times their rated working pressure. This "Safety Factor of 4" is the industry gold standard for preventing accidents during hydraulic surges.
In mechanical rooms filled with vibrating pumps and compressors, piping joints are subject to constant cyclic stress. This can lead to fatigue failure, where a material fails at a pressure well below its rated MAWP because of repeated stress cycles.
The unique metallurgical structure of Jianzhi malleable iron—specifically the "temper carbon" nodules—acts as a natural vibration dampener. As vibrations pass through the iron matrix, the graphite nodules dissipate a portion of the energy as heat. This reduces the mechanical strain on the threaded connections, ensuring that the black pipe fitting maintains its seal for decades, even in high-vibration environments.
All piping materials expand and contract with temperature changes. A 100-meter run of steel pipe can expand by several centimeters when carrying hot oil or steam.
● Coefficient of Expansion: Malleable iron has a thermal expansion coefficient very similar to that of carbon steel pipe.
● Joint Integrity: Because the fitting and the pipe expand at nearly the same rate, the stress on the threaded joint is minimized. This is a significant advantage over using plastic fittings with steel pipes, where mismatched expansion rates often lead to leaks at the interface.
To validate our stress analysis models, Jianzhi subjects its malleable iron pipe fitting line to a series of physical tests that exceed international requirements.
Destructive Burst Testing: We periodically take samples from the production line and pressurize them until failure. A Jianzhi 1-inch elbow typically withstands pressures exceeding 6,000 PSI before bursting—far beyond its Class 150 rating.
● Tensile Testing: We machine test bars from the same melt as our fittings to ensure the tensile strength is between 330–350 MPa.
● Cyclic Pressure Testing: For fittings destined for high-demand sectors like natural gas, we perform cyclic testing to simulate years of pressure fluctuations.
In the interconnected world of modern infrastructure, the black pipe fitting serves as the universal joint. However, for these joints to function, they must speak the correct "language" of threading. At Jianzhi, we recognize that threading is not merely a machining step; it is a critical safety interface that must adhere to strict geometric protocols.
Both BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) and NPT (National Pipe Thread) utilize a 1:16 taper. This means for every 16 units of length, the diameter changes by 1 unit. This taper is the "secret sauce" of a leak-proof connection. As the male pipe enters the malleable iron pipe fitting, the interference between the threads creates a mechanical seal.
The primary difference lies in the thread angle and profile:
● BSPT (ISO 7-1): Features a 55° thread angle with rounded crests and roots. This "Whitworth" form is the standard for most of Europe, Asia, and the Commonwealth. It is exceptionally resilient in high-vibration environments.
● NPT (ASME B1.20.1): Features a 60° thread angle with flat (truncated) crests and roots. This is the North American standard.
Jianzhi’s CNC threading centers are programmed to maintain these angles within a tolerance of ± 0.5°. We use specialized "Master Gauges" to ensure that the pitch diameter is perfect, preventing the common "loose fit" found in inferior cast iron pipe fitting brands.
The black pipe fitting is the silent workhorse of the industrial world. While galvanized fittings are used for water, the "Black" finish is the standard for environments where chemical compatibility and heat resistance are non-negotiable.
In gas systems, the use of galvanized fittings is often prohibited because the gas can cause the zinc coating to flake off, clogging regulators and burners. Black malleable iron is the preferred material due to its:
Zero Porosity: Jianzhi’s high-pressure casting ensures gas molecules cannot seep through the metal.
Shock Resistance: Gas lines in earthquake-prone zones rely on the 10-12% elongation of our fittings to absorb ground shifts without fracturing.
Modern skyscrapers utilize massive steam-fed heating systems. These systems subject fittings to constant thermal cycling—expanding when hot, contracting when cold. Jianzhi's malleable iron pipe fitting products are engineered to withstand temperatures up to 300℃(572°F), far exceeding the capabilities of copper or plastic alternatives.
In a fire, the piping system must not fail. Our black fittings are UL Listed and FM Approved, meaning they have been tested to survive the intense heat of a building fire while maintaining water pressure for the sprinklers. Unlike plastic (CPVC), which melts, or grey iron, which may crack under the thermal shock of cold water hitting hot metal, Jianzhi malleable iron remains structurally sound.
Why do 1 in 3 malleable iron pipe fitting products exported from China carry the Jianzhi mark? It is the result of a massive operational scale combined with a boutique commitment to quality.
Jianzhi operates a production "city." With over 4,000 employees and 350 technical engineers, we produce over 400,000 tons of pipe fittings annually. This scale allows us to:
● Maintain a 25,000-ton permanent stock for 10-15 day delivery.
● Utilize high-cost, high-efficiency Disamatic molding lines from Denmark.
As an "Eco-Friendly" certified manufacturer, Jianzhi leads the industry in green casting.
● Recycling: 90% of our raw material is sourced from high-grade recycled steel scrap.
● Emission Control: Our electric induction furnaces produce 80% less particulate matter than traditional coke-fired cupolas.
● Longevity: A Jianzhi black pipe fitting has a service life exceeding 50 years, reducing the environmental cost of frequent infrastructure replacement.
In the 2025 market, engineers must choose between Malleable Iron, Ductile Iron, and Forged Steel. Here is how they compare:
Feature | Malleable Iron (Jianzhi) | Ductile Iron | Forged Steel |
Manufacturing | Cast & 96hr Annealed | Cast with Magnesium | Hammered/Pressed |
Machinability | Excellent (Ferritic) | Moderate | Difficult |
Impact Resistance | High (12% Elongation) | Very High | Maximum |
Cost | Optimal/Competitive | High | Very High |
Best For | Gas/Steam/Fire (1/8" - 6") | Heavy Mach./Large Pipe | High-Pressure Oil (>3000 PSI) |
While Forged Steel is stronger, it is often 3x the price of a malleable iron pipe fitting. For standard industrial pressures (<300 PSI), Jianzhi malleable iron provides the best safety-to-cost ratio in the world.
Q: Can I use black pipe fittings for drinking (potable) water?
A: No. Without a galvanized coating, the iron will oxidize (rust) over time, discoloring the water. Use Jianzhi Galvanized fittings for potable water.
Q: How many turns should I tighten a Jianzhi fitting?
A: The "Hand-Tight + 2" rule is standard. Tighten by hand until snug, then use a pipe wrench for 1.5 to 2 full turns to engage the taper seal.
Q: What is the difference between a "Light Type" and Jianzhi "Heavy Type"?
A: Light-type fittings reduce wall thickness to save weight. Jianzhi Heavy Type fittings use 15-20% more metal, providing a 4:1 safety factor and a "Zero-Leak" guarantee.
At Hebei Jianzhi Casting Group, we believe that casting is an art form governed by the laws of physics. Since our founding in 1982, we have viewed every black pipe fitting not as a commodity, but as a component of a larger mission: To build a safer, more connected world.
From the 96-hour annealing furnace to the final air-under-water test, our 4,000 employees are dedicated to a single standard—Zero Defects. In an era of disposable products, the Jianzhi malleable iron pipe fitting stands as a testament to the enduring power of quality craftsmanship. When you install a Jianzhi fitting, you are installing peace of mind.
1. ASME B16.3-2021: Malleable Iron Threaded Fittings: Classes 150 and 300. American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
2. ASTM A197/A197M-00(2023): Standard Specification for Cupola Malleable Iron. ASTM International.
3. EN 10242:1995: Threaded pipe fittings in malleable cast iron. European Committee for Standardization.
4. ISO 7-1:2000: Pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are made on the threads — Part 1: Dimensions, tolerances and designation.
5. ASME B1.20.1-2013 (R2018): Pipe Threads, General Purpose (Inch).
6. UL 213: Standard for Rubber Gasketed Fittings for Fire-Protection Service. Underwriters Laboratories.
7. FM Class Number 1112: Approval Standard for Malleable Iron Threaded Fittings. Factory Mutual Research Corporation.
8. ASM Handbook, Volume 1: Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High-Performance Alloys. ASM International, 10th Edition.
9. Davis, J. R. (Ed.) (1996): Cast Irons. ASM International.
10. Hebei Jianzhi Casting Group (2025): Technical Manual for Malleable Iron Fittings: Heavy Type Philosophy and Global Applications.
SAFER
PRODUCT INFO
ABOUT JIANZHI
TECH DATA
Contact Us
E-mail: sales1@jianzhi-fitting.com
Tel: +86 15822792427
Office In Tianjin:
Heping District, Tianjin, China.
Production Base 1:
Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, China.
Production Base 2:
Tangshan City, Hebei Province, China.
Production Base 3:
Schelei Street,Baicoi City,Prahova County,Romania