May. 30, 2024
Malleable and forged fittings are both types of pipe fittings used in plumbing, construction, and industrial applications, but they differ in terms of their manufacturing processes, material properties, and applications. Here's a detailed comparison:

Material: Made from cast iron that has been annealed (a heat treatment process).
Process: The cast iron is heated for an extended period, which converts the brittle structure into a malleable iron, giving it greater ductility and impact resistance.
Forming: These fittings are often molded and then annealed to achieve the desired properties.
Material: Typically made from carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel.
Process: The metal is heated to a high temperature and then hammered or pressed into shape. This process aligns the grain structure of the metal and enhances its strength and durability.
Forming: Forging produces very strong and reliable fittings, often used for high-pressure applications.
Strength: Generally have good strength and are less brittle than regular cast iron.
Ductility: More ductile than cast iron but less so than forged steel.
Corrosion Resistance: Decent, but it can vary depending on the environment and any coatings applied.
Surface Finish: Typically smoother than cast iron but not as smooth as forged fittings.
Strength: Very high strength due to the forging process.
Ductility: Higher ductility compared to malleable fittings, making them suitable for high-stress applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Often better than malleable fittings, especially if made from stainless steel or alloy steel.
Surface Finish: Generally smoother and more precise due to the forging process.
Pressure Rating: Suitable for low to medium pressure applications.
Uses: Commonly used in plumbing, heating, and air conditioning systems, and in general utility services for water, gas, and steam.
Cost: Typically less expensive than forged fittings.

Pressure Rating: Suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Uses: Commonly used in chemical, petroleum, and gas industries, and in high-pressure steam and hydraulic systems.
Cost: Generally more expensive due to the more intensive manufacturing process and higher material quality.
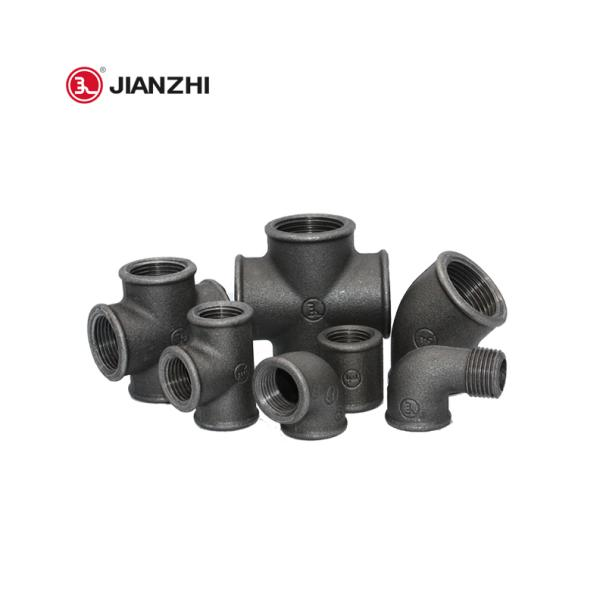
Common types include elbows, tees, couplings, unions, and bushings.
Often come in black or galvanized finishes for different applications.
Common types include elbows, tees, crosses, couplings, plugs, and caps.
Available in different pressure ratings such as Class 2000, 3000, and 6000.
Malleable fittings are made from cast iron that is heat-treated to become ductile and are typically used in low to medium pressure applications.
Forged fittings are made from steel that is hammered or pressed into shape, resulting in high strength and ductility, and are suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Choosing between malleable and forged fittings depends on the specific requirements of the application, including pressure, temperature, cost, and durability considerations.
SAFER
PRODUCT INFO
ABOUT JIANZHI
TECH DATA
Contact Us
E-mail: sales1@jianzhi-fitting.com
Tel: +86 15822792427
Office In Tianjin:
Heping District, Tianjin, China.
Production Base 1:
Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, China.
Production Base 2:
Tangshan City, Hebei Province, China.
Production Base 3:
Schelei Street,Baicoi City,Prahova County,Romania