Feb. 09, 2026
In the pipeline system, the distinction between male and female connectors is a key factor in ensuring safe connection, reliable sealing and system compatibility. The following is a detailed analysis of male and female connectors, covering definitions, structural features, performance characteristics, application scenarios, standard specifications and selection recommendations, to help you deeply understand and correctly choose the appropriate connector type.
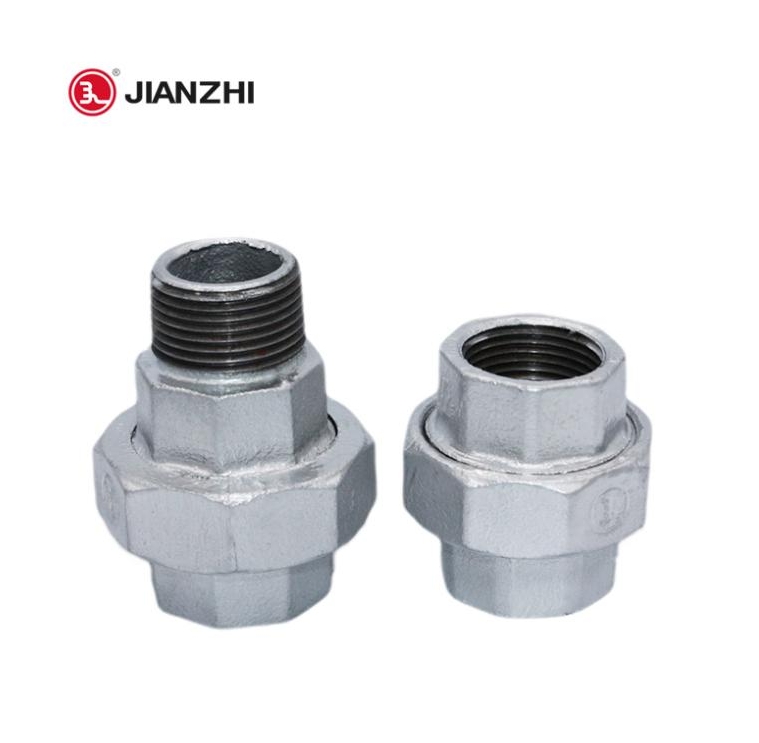

● Male: refers to a connector with external threads, whose threads are located on the outer surface of the component and are usually used to insert into the inside of the female connector.
● Female: refers to a connector with internal threads, whose threads are located on the inner surface of the component and are designed to accept the insertion of the male connector.
This matching method ensures the firmness and sealing of the connection and is a common connection form in the pipeline system.
Structural features: The threads are located on the outside, usually cylindrical or conical, with spiral lines on the surface, which increases the friction and sealing performance during connection. Cylindrical threads are generally non-sealed threads, and conical threads are sealed threads. Conical threads are generally used in fire protection and water fields.
● Strong sealing: usually adopt metal ring and sealing ring design to ensure the sealing performance of pipe fittings and effectively prevent fluid leakage. Raw tape or hemp rope will be used for auxiliary sealing during installation to ensure perfect sealing effect.
● High temperature resistance and corrosion resistance: mostly made of high-quality materials, with excellent high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, suitable for various harsh environments.
● Easy installation: As the preload increases, the compression force of the thread contact surface increases, and the friction resistance increases accordingly. According to the principle of thread self-locking, when the thread lead angle (α) is less than the friction angle (β'), the friction torque is sufficient to prevent loosening, but at the same time, a larger torque is required to continue tightening, making the installation and disassembly process quick and convenient, and improving work efficiency.
Structural features: The thread is located inside and is designed for the insertion of the male connector. Usually, a tapered thread structure is used inside to ensure the sealing of the connection.
● Sealed transmission: The internal tapered thread structure ensures that the medium will not leak during the transmission process.
● Strong corrosion resistance: mostly made of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or high-strength plastic, which can resist the erosion of various corrosive media.
● Various specifications: A variety of specifications are available to meet the needs of different pipe diameters and realize flexible and diverse connection solutions.
Proper installation and selection are key to maximizing the performance of female fitting and male female plumbing fittings. Follow these guidelines to avoid common issues and ensure system safety.
- Clean Threads First: Before installation, clean the internal threads of thefemale fitting and the external threads of the male fitting to remove dirt, rust, or debris—this prevents thread damage and ensures a tight seal.
- Use Sealing Materials Appropriately: For tapered threads (NPT/BSPT), wrap 3-5 turns of PTFE tape around the male fitting’s external thread (clockwise direction) before inserting into the female fitting. For cylindrical threads (G thread), use a rubber gasket or sealant.
- Control Torque: Tighten the male female plumbing fittings with a wrench to the appropriate torque—over-tightening will damage the threads, while under-tightening will cause leakage. For small-size female fitting (≤1”), hand-tightening plus 1/4 turn is sufficient; for larger sizes, use a torque wrench.
- Check for Leakage: After installation, test the pipeline with water or air pressure to check for leakage at the male female plumbing fittings connection. If leakage occurs, re-tighten or replace the female fitting and male fitting.
Same Standard Requirement: Male female plumbing fittings must comply with the same thread standard (NPT/BSPT/G). For example, an NPT female fitting can only be paired with an NPT male fitting—mixing standards (e.g., NPT female + BSPT male) will cause thread mismatch and leakage.
Same Size Compatibility: The nominal size of the male and female fittings must be consistent. A 1/2” female fitting should be paired with a 1/2” male fitting to ensure proper insertion depth and thread engagement.
Pressure & Temperature Matching: The pressure and temperature ratings of male female plumbing fittings must meet the working conditions of the pipeline. For high-pressure steam systems, select high-pressure resistant female fitting and male fittings to avoid structural damage.
☑ Water system and fire protection system: Male pipe fittings are threaded with female valves, faucets, connectors and other components, often supplemented with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) raw tape or sealant to ensure no water leakage.
☑ Steam system and HVAC system: High-pressure hydraulic hoses often use male connectors to match the female connectors on the pump body or actuator to form a reliable high-pressure seal.
☑ Gas and fuel pipelines: National standards (such as US NPT, European BSPT/BSPP) specify thread specifications and genders to ensure that only male and female heads of the same standard and size can be paired to avoid leakage or safety hazards.
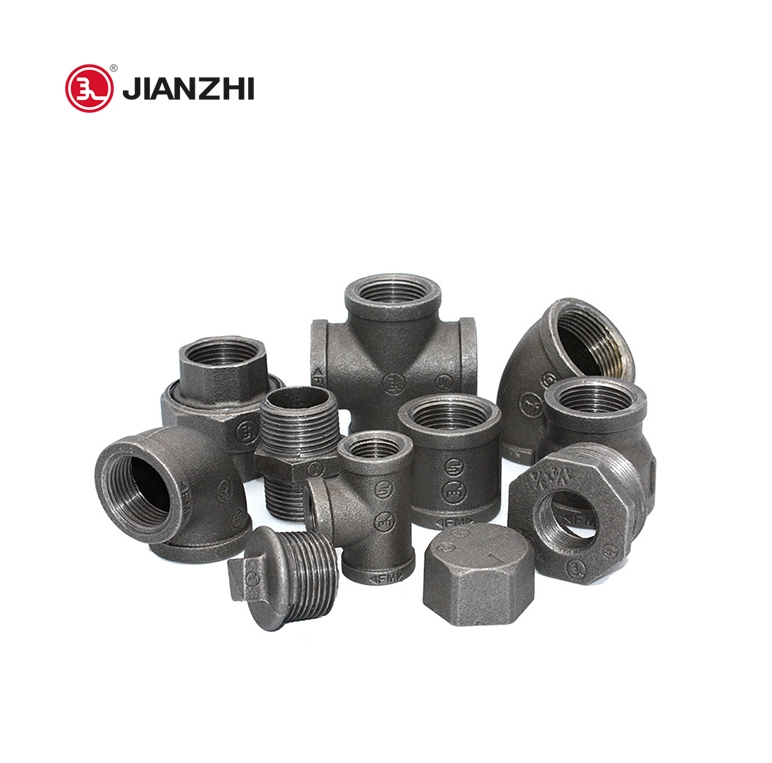

● NPT (National Pipe Thread): US standard 60-degree tapered pipe thread, used in the Americas, the Middle East and the Philippines.
● BSPT (Pipe Thread): 55-degree sealed tapered pipe thread, belongs to the Whitworth thread family, mostly used in Europe, Asia and Oceania.
● G thread: 55 degree non-threaded sealing pipe thread, belongs to the Whitworth thread family, marked as G for cylindrical thread.
In addition, the thread size mark (such as 1/4, 1/2, 1/8) refers to the diameter of the thread size, in inches.
→ Clear application requirements: Select the appropriate connector type and material according to factors such as media type, working pressure, temperature, etc.
→ Match thread standards: Ensure that the thread standards of male and female connectors are consistent to avoid poor connection or leakage.
→ Consider installation space: Select connectors of appropriate size and structure according to the space limitations of the installation environment.
→ Pay attention to sealing performance: For high-pressure or leak-prone systems, choose connectors with excellent sealing performance and use sealing materials in combination.
→ Choose a reliable brand: High-quality connector products can provide better performance and longer service life, reducing maintenance costs.
International Certification: ISO9001, API, CE certified, complying with global industry standards.
High-Quality Materials: Strict material selection to ensure durability and performance in various environments.
Customization Service: Customize female fitting and male female plumbing fittings according to your size, material, and thread standard requirements.
Global Application Cases: Our female fitting and male female plumbing fittings are widely used in water, fire, gas, and industrial projects in the USA, Europe, Australia, and other regions.
24/7 Customer Support: Professional team provides technical advice and after-sales service via WhatsApp, Email, and Skype.
Through the above detailed analysis, you can have a more comprehensive understanding of the difference between male and female connectors and their application in pipeline systems, helping you make more reasonable choices in actual projects.
SAFER
PRODUCT INFO
ABOUT JIANZHI
TECH DATA
Contact Us
E-mail: sales1@jianzhi-fitting.com
Tel: +86 15822792427
Office In Tianjin:
Heping District, Tianjin, China.
Production Base 1:
Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, China.
Production Base 2:
Tangshan City, Hebei Province, China.
Production Base 3:
Schelei Street,Baicoi City,Prahova County,Romania